Silicone sealant is a versatile material used extensively in sealing and bonding applications. However, silicone sealants will not adhere to certain surfaces and materials. Understanding these limitations is critical to achieving successful and long-lasting sealing and bonding results. In this blog, we will explore the factors that affect silicone sealant adhesion and provide solutions for treating silicone sealant non-stick surfaces.


Q: What doesn’t silicone sealant stick to?
A: Silicone sealants may not adhere well to certain surfaces, including:
1. Non-porous materials: Silicone sealants do not bond well to non-porous surfaces such as glass, metal, and plastic. The low surface energy of these surfaces makes it difficult for silicones to form strong bonds.
2. PTFE and other fluoropolymer-based materials: PTFE and other fluoropolymer-based materials are known for their non-stick properties, which also make them resistant to silicone sticking.
3. Contaminated surfaces: Silicone sealant will not adhere to surfaces contaminated by oil, grease or other substances. Proper surface preparation is essential to ensure good adhesion.
4. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene: These plastics have low surface energy and are difficult to bond with silicone sealants.
Q: What are some solutions for treating surfaces where silicone sealant won’t stick?
A: While silicone sealants may not adhere well to some surfaces, there are some solutions that can improve adhesion and ensure a successful bond:
1. Surface Preparation: Proper surface preparation is essential to promote adhesion. The surface should be clean, dry and free of any contaminants such as oil, grease or dust. Use a suitable solvent or cleaner to remove any contaminants before applying silicone sealant.
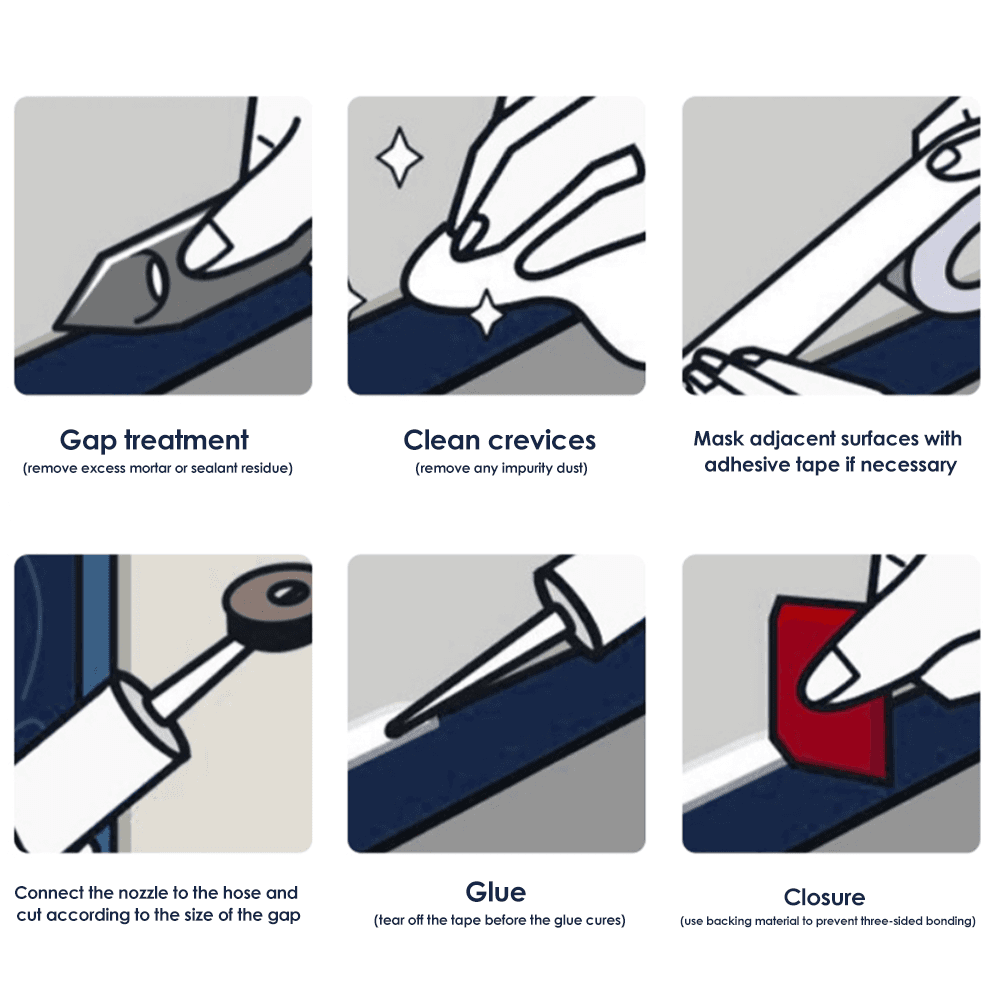
2. Use a primer: If silicone sealant is having difficulty adhering to a specific surface, using a primer can significantly improve adhesion. Primers are designed to enhance the bonding properties of silicone sealants on difficult-to-bond surfaces such as plastics and metals.
3. Mechanical bonding: For non-porous surfaces such as glass and metal, creating mechanical bonding can improve adhesion. This can be accomplished by using methods such as sanding or roughening the surface to provide a better grip for the silicone sealant.
4. Choose the right silicone sealant: Not all silicone sealants are suitable for all surfaces. It is important to choose a silicone sealant that is formulated specifically for the type of surface you are working on. There are specialized silicone sealants available for bonding plastic, metal, and other challenging surfaces.
While silicone sealant is a versatile and effective sealing and bonding material, it is important to be aware of its limitations in bonding to certain surfaces. By understanding these limitations and implementing appropriate solutions, it is possible to achieve strong and long-lasting bonds using silicone sealants, even on challenging surfaces. Proper surface preparation, use of primer, and selection of the correct silicone sealant are key factors in overcoming bonding challenges and ensuring a successful sealing and bonding application.
Post time: May-29-2024