1, Hydroxyl value: 1 gram polymer polyol contained hydroxyl (-OH) amount equivalent to the number of milligrams of KOH, the unit mgKOH/g.
2, Equivalent: the average molecular weight of a functional group.
3, Isocyanate content: the content of isocyanate in the molecule
4, Isocyanate index: indicates the degree of isocyanate excess in the polyurethane formula, usually represented by the letter R.
5. Chain extender: It refers to low molecular weight alcohols and amines that can extend, expand or form spatial network crosslinks of molecular chains.
6. Hard segment: The chain segment formed by the reaction of isocyanate, chain extender and crosslinker on the main chain of polyurethane molecules, and these groups have larger cohesion energy, larger space volume and greater rigidity.
7, Soft segment: carbon carbon main chain polymer polyol, flexibility is good, in the polyurethane main chain for the flexible chain segment.
8, One-step method: refers to the oligomer polyol, diisocyanate, chain extender and catalyst mixed at the same time after direct injection into the mold, at a certain temperature curing molding method.
9, Prepolymer method: First oligomer polyol and diisocyanate prepolymerization reaction, to generate end NCO based polyurethane prepolymer, pouring and then prepolymer reaction with chain extender, preparation of polyurethane elastomer method, called prepolymer method.
10, Semi-prepolymer method: the difference between the semi-prepolymer method and the prepolymer method is that part of the polyester polyol or polyether polyol is added to the prepolymer in the form of a mixture with chain extender, catalyst, etc.
11, Reaction injection molding: Also known as Reaction Injection Moulding RIM(Reaction Injection Moulding), it is measured by oligomers with low molecular weight in liquid form, instantly mixed and injected into the mold at the same time, and the rapid reaction in the mold cavity, the molecular weight of the material increases rapidly. A process for generating entirely new polymers with new characteristic group structures at extremely high speeds.
12, Foaming index: that is, the number of parts of water used in 100 parts of polyether is defined as foaming index (IF).
13, Foaming reaction: generally refers to the reaction of water and isocyanate to produce substituted urea and release CO2.
14, Gel reaction: generally refers to the formation of carbamate reaction.
15, Gel time: under certain conditions, the liquid material to form gel required time.
16, Milky time: at the end of zone I, milky phenomenon appears in the liquid phase polyurethane mixture. This time is called cream time in the generation of polyurethane foam.
17, Chain expansion coefficient: refers to the ratio of the amount of amino and hydroxyl groups (unit: mo1) in the chain extender components (including the mixed chain extender) to the amount of NCO in the prepolymer, that is, the mole number (equivalent number) ratio of the active hydrogen group to NCO.
18, Low unsaturation polyether: mainly for PTMG development, PPG price, unsaturation reduced to 0.05mol/kg, close to the performance of PTMG, using DMC catalyst, the main variety of Bayer Acclaim series products.
19, Ammonia ester grade solvent: the production of polyurethane solvent to consider the dissolution force, volatilization rate, but the production of polyurethane used in the solvent, should focus on taking into account the heavy NC0 in polyurethane. Solvents such as alcohols and ether alcohols that react with NCO groups cannot be selected. The solvent can not contain impurities such as water and alcohol, and can not contain alkali substances, which will make the polyurethane deteriorate.
The ester solvent is not allowed to contain water, and must not contain free acids and alcohols, which will react with NCO groups. The ester solvent used in polyurethane should be "ammonia ester grade solvent" with high purity. That is, the solvent reacts with excess isocyanate, and then the amount of unreacted isocyanate is determined with dibutylamine to test whether it is suitable for use. The principle is that the consumption of isocyanate is not applicable, because it shows that the water in the ester, alcohol, acid three will consume the total value of isocyanate, if the number of grams of solvent required to consume leqNCO group is expressed, the value is good stability.
Isocyanate equivalent less than 2500 is not used as a polyurethane solvent.
The polarity of the solvent has a great influence on the reaction of resin formation. The greater the polarity, the slower the reaction, such as toluene and methyl ethyl ketone difference of 24 times, this solvent molecule polarity is large, can form a hydrogen bond with the alcohol hydroxyl group and make the reaction slow.
Polychlorinated ester solvent is better to choose aromatic solvent, their reaction speed is faster than ester, ketone, such as xylene. The use of ester and ketone solvents can extend the service life of the double-branched polyurethane during construction. In the production of coatings, the selection of the "ammonia-grade solvent" mentioned earlier is beneficial to the stored stabilizers.
Ester solvents have strong solubility, moderate volatilization rate, low toxicity and are used more, cyclohexanone is also used more, hydrocarbon solvents have low solid dissolution ability, less use alone, and more use with other solvents.
20, Physical blowing agent: physical blowing agent is the foam pores are formed through the change of the physical form of a substance, that is, through the expansion of compressed gas, the volatilization of liquid or the dissolution of solid.
21, Chemical blowing agents: chemical blowing agents are those that can release gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen after heating decomposition, and form fine pores in the polymer composition of the compound.
22, Physical crosslinking: there are some hard chains in the polymer soft chain, and the hard chain has the same physical properties as the vulcanized rubber after chemical crosslinking at the temperature below the softening point or melting point.
23, Chemical crosslinking: refers to the process of linking large molecular chains through chemical bonds under the action of light, heat, high-energy radiation, mechanical force, ultrasound and crosslinking agents to form a network or shape structure polymer.
24, Foaming index: the number of parts of water equivalent to 100 parts of polyether is defined as foaming index (IF).
25. What types of isocyanates are commonly used in terms of structure?
A: Aliphatic: HDI, alicyclic: IPDI,HTDI,HMDI, Aromatic: TDI,MDI,PAPI,PPDI,NDI.
26. What kinds of isocyanates are commonly used? Write the structural formula
A: Toluene diisocyanate (TDI), diphenylmethane-4,4 '-diisocyanate (MDI), polyphenylmethane polyisocyanate (PAPI), liquefied MDI, hexamethylene-diisocyanate (HDI).
27. Meaning of TDI-100 and TDI-80?
A: TDI-100 is composed of toluene diisocyanate with 2,4 structure; TDI-80 refers to a mixture consisting of 80% toluene diisocyanate of 2,4 structure and 20% of 2,6 structure.
28. What are the characteristics of TDI and MDI in the synthesis of polyurethane materials?
A: Reactivity for 2,4-TDI and 2,6-TDI. The reactivity of 2,4-TDI is several times higher than that of 2,6-TDI, because the 4-position NCO in 2,4-TDI is far away from the 2-position NCO and methyl group, and there is almost no steric resistance, while the NCO of 2,6-TDI is affected by the steric effect of ortho-methyl group.
The two NCO groups of MDI are far apart and there are no substituents around, so the activity of the two NCO is relatively large. Even if one NCO participates in the reaction, the activity of the remaining NCO is decreased, and the activity is still relatively large in general. Therefore, the reactivity of MDI polyurethane prepolymer is larger than that of TDI prepolymer.
29.HDI, IPDI, MDI, TDI, NDI which of the yellowing resistance is better?
A: HDI(belongs to the invariant yellow aliphatic diisocyanate), IPDI(made of polyurethane resin with good optical stability and chemical resistance, generally used to manufacture high-grade non-discoloration polyurethane resin).
30. Purpose of MDI modification and common modification methods
A: Liquefied MDI: Modified purpose: liquefied pure MDI is a liquefied modified MDI, which overcomes some defects of pure MDI (solid at room temperature, melting when used, multiple heating affects the performance), and also provides the basis for a wide range of modifications for the improvement and improvement of the performance of MDI-based polyurethane materials.
Methods:
① urethane modified liquefied MDI.
② carbodiimide and uretonimine modified liquefied MDI.
31. What types of polymer polyols are commonly used?
A: Polyester polyol, polyether polyol
32. How many industrial production methods are there for polyester polyols?
A: Vacuum melting method B, carrier gas melting method C, azeotropic distillation method
33. What are the special structures on the molecular backbone of polyester and polyether polyols?
A: Polyester polyol: A macromolecular alcohol compound containing an ester group on the molecular backbone and a hydroxyl group (-OH) on the end group. Polyether polyols: Polymers or oligomers containing ether bonds (-O-) and end bands (-Oh) or amine groups (-NH2) in the backbone structure of the molecule.
34. What are the types of polyether polyols according to their characteristics?
A: Highly active polyether polyols, grafted polyether polyols, flame retardant polyether polyols, heterocyclic modified polyether polyols, polytetrahydrofuran polyols.
35. How many kinds of ordinary polyethers are there according to the starting agent?
A: Polyoxide propylene glycol, polyoxide propylene triol, hard bubble polyether polyol, low unsaturation polyether polyol.
36. What is the difference between hydroxy-terminated polyethers and amine-terminated polyethers?
Aminoterminated polyethers are polyoxide allyl ethers in which the hydroxyl end is replaced by an amine group.
37. What kinds of polyurethane catalysts are commonly used? Which commonly used varieties are included?
A: Tertiary amine catalysts, commonly used varieties are: triethylenediamine, dimethylethanolamine, n-methylmorpholine,N, n-dimethylcyclohexamine
Metallic alkyl compounds, commonly used varieties are: organotin catalysts, can be divided into stannous octoate, stannous oleate, dibutyltin dilaurate.
38. What are the commonly used polyurethane chain extenders or crosslinkers?
A: Polyols (1, 4-butanediol), alicyclic alcohols, aromatic alcohols, diamines, alcohol amines (ethanolamine, diethanolamine)
39. Reaction mechanism of isocyanates
A: The reaction of isocyanates with active hydrogen compounds is caused by the nucleophilic center of the active hydrogen compound molecule attacking the NCO based carbon atom. The reaction mechanism is as follows:
40. How does the structure of isocyanate affect the reactivity of NCO groups?
A: The electronegativity of the A.R group: if the R group is an electron absorbing group, the electron cloud density of the C atom in the -NCO group is lower, and it is more vulnerable to the attack of nucleophiles, that is, it is easier to carry out nucleophilic reactions with alcohols, amines and other compounds. If R is an electron donor group and is transferred through the electron cloud, the electron cloud density of the C atom in the -NCO group will increase, making it less vulnerable to the attack of nucleophiles, and its reaction ability with active hydrogen compounds will decrease. B. Induction effect: Because the aromatic diisocyanate contains two NCO groups, when the first -NCO gene participates in the reaction, due to the conjugated effect of the aromatic ring, the -NCO group that does not participate in the reaction will play the role of electron absorbing group, so that the reaction activity of the first NCO group is enhanced, which is the induction effect. C. steric effect: In aromatic diisocyanate molecules, if two -NCO groups are in an aromatic ring at the same time, then the influence of one NCO group on the reactivity of the other NCO group is often more significant. However, when two NCO groups are located in different aromatic rings in the same molecule, or they are separated by hydrocarbon chains or aromatic rings, the interaction between them is small, and it decreases with the increase of the length of the chain hydrocarbon or the increase of the number of aromatic rings.
41. Types of active hydrogen compounds and NCO reactivity
A: Aliphatic NH2> Aromatic group Bozui OH> Water > Secondary OH> Phenol OH> Carboxyl group > Substituted urea > Amido> Carbamate. (If the electron cloud density of the nucleophilic center is higher, the electronegativity is stronger, and the reaction activity with isocyanate is higher and the reaction speed is faster; Otherwise, the activity is low.)
42. Influence of hydroxyl compounds on their reactivity with isocyanates
A: The reactivity of active hydrogen compounds (ROH or RNH2) is related to the properties of R, when R is an electron-withdrawing group (low electronegativity), it is difficult to transfer hydrogen atoms, and the reaction between active hydrogen compounds and NCO is more difficult; If R is an electron-donating substituent, the reactivity of active hydrogen compounds with NCO can be improved.
43. What is the use of isocyanate reaction with water
A: It is one of the basic reactions in the preparation of polyurethane foam. The reaction between them first produces an unstable carbamic acid, which then breaks down into CO2 and amines, and if the isocyanate is in excess, the resulting amine reacts with the isocyanate to form a urea.
44. In the preparation of polyurethane elastomers, the water content of polymer polyols should be strictly controlled
A: No bubbles are required in elastomers, coatings and fibers, so the water content in raw materials must be strictly controlled, usually less than 0.05%.
45. Differences in catalytic effects of amine and tin catalysts on isocyanate reactions
A: Tertiary amine catalysts have high catalytic efficiency for the reaction of isocyanate with water, while tin catalysts have high catalytic efficiency for the reaction of isocyanate with hydroxyl group.
46. Why can polyurethane resin be regarded as a block polymer, and what are the characteristics of the chain structure?
Answer: Because the chain segment of polyurethane resin is composed of hard and soft segments, the hard segment refers to the chain segment formed by the reaction of isocyanate, chain extender and crosslinker on the main chain of polyurethane molecules, and these groups have larger cohesion energy, larger space volume and greater rigidity. The soft segment refers to the carbon-carbon main chain polymer polyol, which has good flexibility and is a flexible segment in the polyurethane main chain.
47. What are the factors that affect the properties of polyurethane materials?
A: Group cohesion energy, hydrogen bond, crystallinity, crosslinking degree, molecular weight, hard segment, soft segment.
48. What raw materials are the soft and hard segments on the main chain of polyurethane materials
A: The soft segment is composed of oligomer polyols (polyester, polyether diols, etc.), and the hard segment is composed of polyisocyanates or their combination with small molecule chain extenders.
49. How do soft segments and hard segments affect the properties of polyurethane materials?
A: Soft segment: (1) The molecular weight of the soft segment: assuming that the molecular weight of the polyurethane is the same, if the soft segment is polyester, the strength of the polyurethane will increase with the increase of the molecular weight of the polyester diol; If the soft segment is polyether, the strength of polyurethane decreases with the increase of the molecular weight of polyether diol, but the elongation increases. (2) The crystallinity of the soft segment: It has a greater contribution to the crystallinity of the linear polyurethane chain segment. In general, crystallization is beneficial for improving the performance of polyurethane products, but sometimes crystallization reduces the low temperature flexibility of the material, and the crystalline polymer is often opaque.
Hard segment: The hard chain segment usually affects the softening and melting temperature and high temperature properties of the polymer. Polyurethanes prepared by aromatic isocyanates contain rigid aromatic rings, so the polymer strength in the hard segment increases, and the material strength is generally larger than that of aliphatic isocyanate polyurethanes, but the resistance to ultraviolet degradation is poor, and it is easy to yellowing. Aliphatic polyurethanes do not yellow.
50. Polyurethane foam classification
A: (1) hard foam and soft foam, (2) high density and low density foam, (3) polyester type, polyether type foam, (4) TDI type, MDI type foam, (5) polyurethane foam and polyisocyanurate foam, (6) one-step method and prepolymerization method production, continuous method and intermittent production, (8) block foam and molded foam.
51. Basic reactions in foam preparation
A: It refers to the reaction of -NCO with -OH, -NH2 and H2O, and when reacting with polyols, the "gel reaction" in the foaming process generally refers to the formation reaction of carbamate. Because the foam raw material uses multi-functional raw materials, a cross-linked network is obtained, which allows the foaming system to gel quickly.
The foaming reaction occurs in the foaming system with the presence of water. The so-called "foaming reaction" generally refers to the reaction of water and isocyanate to produce substituted urea and release CO2.
52. Nucleation mechanism of bubbles
The raw material reacts in a liquid or depends on the temperature produced by the reaction to produce a gaseous substance and volatilize the gas. With the progress of the reaction and the production of a large amount of reaction heat, the amount of gaseous substances and volatilization increased continuously. When the gas concentration increases beyond the saturation concentration, a sustained bubble begins to form in the solution phase and rises.
53. The role of foam stabilizer in the preparation of polyurethane foam
A: It has the emulsification effect, so that the mutual solubility between the components of the foam material is enhanced; After the addition of silicone surfactant, because it greatly reduces the surface tension γ of the liquid, the increased free energy required for gas dispersion is reduced, so that the air dispersed in the raw material is more likely to nucleate during the mixing process, which contributes to the production of small bubbles and improves the stability of the foam.
54. Stability mechanism of foam
A: The addition of appropriate surfactants is conducive to the formation of fine bubble dispersion.
55. Formation mechanism of open cell foam and closed cell foam
A: The formation mechanism of open-cell foam: In most cases, when there is a large pressure in the bubble, the strength of the bubble wall formed by the gel reaction is not high, and the wall film can not withstand the stretching caused by the rising gas pressure, the bubble wall film is pulled, and the gas escapes from the rupture, forming the open-cell foam.
Closed-cell foam formation mechanism: For the hard bubble system, due to the reaction of polyether polyols with multi-functional and low molecular weight with polyisocyanate, the gel speed is relatively fast, and the gas in the bubble can not break the bubble wall, thus forming the closed-cell foam.
56. Foaming mechanism of physical foaming agent and chemical foaming agent
A: Physical blowing agent: The physical blowing agent is the foam pores are formed through the change of the physical form of a certain substance, that is, through the expansion of compressed gas, the volatilization of liquid or the dissolution of solid.
Chemical blowing agents: Chemical blowing agents are compounds that, when decomposed by heat, release gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen and form fine pores in the polymer composition.
57. Preparation method of soft polyurethane foam
A: One-step method and prepolymer method
Prepolymer method: that is, the polyether polyol and excess TDI reaction is made into a prepolymer containing free NCO group, and then mixed with water, catalyst, stabilizer, etc., to make foam. One-step method: A variety of raw materials are directly mixed into the mixing head through calculation, and a step is made of foam, which can be divided into continuous and intermittent.
58. Characteristics of horizontal foaming and vertical foaming
Balanced pressure plate method: characterized by the use of top paper and top cover plate. Overflow groove method: characterized by the use of overflow groove and conveyor belt landing plate.
Vertical foaming characteristics: you can use a small flow to get a large cross-sectional area of foam blocks, and usually use a horizontal foaming machine to get the same section of the block, the flow level is 3 to 5 times larger than the vertical foaming; Because of the large cross section of the foam block, there is no upper and lower skin, and the edge skin is also thin, so the cutting loss is greatly reduced. The equipment covers a small area, the plant height is about 12 ~ 13m, and the investment cost of the plant and equipment is lower than that of the horizontal foaming process; It is easy to replace the hopper and the model to produce cylindrical or rectangular foam bodies, especially round foam billets for rotary cutting.
59. Basic points of raw material selection for soft foaming preparation
A: Polyol: polyether polyol for ordinary block foam, molecular weight is generally 3000 ~ 4000, mainly polyether triol. Polyether triol with molecular weight of 4500 ~ 6000 is used for high resilience foam. With the increase of molecular weight, the tensile strength, elongation and resilience of the foam increase. The reactivity of similar polyethers decreased. With the increase of the functional degree of polyether, the reaction is relatively accelerated, the crosslinking degree of polyurethane is increased, the foam hardness is increased, and the elongation is decreased. Isocyanate: The isocyanate raw material of polyurethane soft block foam is mainly toluene diisocyanate (TDI-80). The relatively low activity of TDI-65 is only used for polyester polyurethane foam or special polyether foam. Catalyst: The catalytic benefits of bulk soft foam foaming can be roughly divided into two categories: one is organometallic compounds, stannous caprylate is the most commonly used; Another type is tertiary amines, commonly used as dimethylaminoethyl ethers. Foam stabilizer: In polyester polyurethane bulk foam, non-silicon surfactants are mainly used, and in polyether bulk foam, organosilica-oxidized olefin copolymer is mainly used. Foaming agent: In general, only water is used as foaming agent when the density of polyurethane soft block bubbles is greater than 21 kg per cubic meter; Low boiling point compounds such as methylene chloride (MC) are used as auxiliary blowing agents only in low density formulations.
60. Influence of environmental conditions on the physical properties of block foams
A: The effect of temperature: the foaming reaction of polyurethane accelerates as the material temperature rises, which will cause the risk of core burning and fire in sensitive formulations. The influence of air humidity: With the increase of humidity, due to the reaction of isocyanate group in the foam with water in the air, the hardness of the foam decreases and the elongation increases. The tensile strength of the foam increases with the increase of the urea group. The effect of atmospheric pressure: For the same formula, when foaming at a higher altitude, the density is significantly reduced.
61. The main difference between the raw material system used for cold molded soft foam and hot molded foam
A: The raw materials used in cold curing molding have high reactivity, and there is no need for external heating during curing, relying on the heat generated by the system, the curing reaction can be basically completed in a short time, and the mold can be released within a few minutes after the injection of raw materials. The raw material reactivity of hot curing molding foam is low, and the reaction mixture needs to be heated together with the mold after foaming in the mold, and the foam product can be released after it is fully matured in the baking channel.
62. What are the characteristics of cold-molded soft foam compared with hot-molded foam
A: ① The production process does not require external heat, can save a lot of heat; ② High sag coefficient (collapsibility ratio), good comfort performance; ③ High rebound rate; ④ Foam without flame retardant also has certain flame retardant properties; ⑤ Short production cycle, can save mold, save cost.
63. Characteristics and uses of soft bubble and hard bubble respectively
A: Characteristics of soft bubbles: The cell structure of polyurethane soft bubbles is mostly open. Generally, it has low density, good elastic recovery, sound absorption, air permeability, heat preservation and other properties. Uses: Mainly used for furniture, cushion material, vehicle seat cushion material, a variety of soft padding laminated composite materials, industrial and civil soft foam is also used as filter materials, sound insulation materials, shock-proof materials, decorative materials, packaging materials and thermal insulation materials.
Characteristics of rigid foam: polyurethane foam has light weight, high specific strength and good dimensional stability; The thermal insulation performance of polyurethane rigid foam is superior. Strong adhesive force; Good aging performance, long adiabatic service life; The reaction mixture has good fluidity and can fill the cavity or space of complex shape smoothly. The raw material of polyurethane hard foam production has high reactivity, can achieve rapid curing, and can achieve high efficiency and mass production in the factory.
Uses: Used as insulation material for refrigerators, freezers, refrigerated containers, cold storage, oil pipeline and hot water pipeline insulation, building wall and roof insulation, insulation sandwich board, etc.
64. Key points of hard bubble formula design
A: Polyols: polyether polyols used for hard foam formulations are generally high energy, high hydroxyl value (low molecular weight) polypropylene oxide polyols; Isocyanate: At present, the isocyanate used for hard bubbles is mainly polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate (generally known as PAPI), that is, crude MDI and polymerized MDI; Blowing agents :(1)CFC blowing agent (2)HCFC and HFC blowing agent (3) pentane blowing agent (4) water; Foam stabilizer: The foam stabilizer used for polyurethane rigid foam formulation is generally a block polymer of polydimethylsiloxane and polyoxolefin. At present, most foam stabilizers are mainly Si-C type; Catalyst: The catalyst of hard bubble formulation is mainly tertiary amine, and organotin catalyst can be used in special occasions; Other additives: According to the requirements and needs of different uses of polyurethane rigid foam products, flame retardants, opening agents, smoke inhibitors, anti-aging agents, anti-mildew agents, toughening agents and other additives can be added to the formula.
65. Whole skin molding foam preparation principle
A: integral skin foam (ISF), also known as self skinning foam (self skinning foam), is a plastic foam that produces its own dense skin at the time of manufacture.
66. Characteristics and uses of polyurethane microporous elastomers
A: Characteristics: polyurethane elastomer is a block polymer, generally composed of oligomer polyol flexible long chain soft segment, diisocyanate and chain extender to form a hard segment, hard segment and soft segment alternate arrangement, forming a repetitive structural unit. In addition to containing ammonia ester groups, the polyurethane can form hydrogen bonds within and between molecules, and the soft and hard segments can form microphase regions and produce microphase separation.
67. What are the main performance characteristics of polyurethane elastomers
A: Performance characteristics: 1, high strength and elasticity, can be in a wide range of hardness (Shaw A10 ~ Shaw D75) to maintain a high elasticity; Generally, the required low hardness can be achieved without plasticizer, so there is no problem caused by plasticizer migration; 2, under the same hardness, higher carrying capacity than other elastomers; 3, excellent wear resistance, its wear resistance is 2 to 10 times that of natural rubber; 4. Excellent oil and chemical resistance; Aromatic polyurethane radiation resistant; Excellent oxygen resistance and ozone resistance; 5, high impact resistance, good fatigue resistance and shock resistance, suitable for high-frequency flexure applications; 6, low temperature flexibility is good; 7, ordinary polyurethane can not be used above 100 ℃, but the use of special formula can withstand 140 ℃ high temperature; 8, molding and processing costs are relatively low.
68. Polyurethane elastomers are classified according to polyols, isocyanates, manufacturing processes, etc
A: 1. According to the raw material of oligomer polyol, polyurethane elastomers can be divided into polyester type, polyether type, polyolefin type, polycarbonate type, etc. Polyether type can be divided into polytetrahydrofuran type and polypropylene oxide type according to specific varieties; 2. According to the difference of diisocyanate, it can be divided into aliphatic and aromatic elastomers, and subdivided into TDI type, MDI type, IPDI type, NDI type and other types; From the manufacturing process, polyurethane elastomers are traditionally divided into three categories: casting type (CPU), thermoplasticity (TPU) and mixing type (MPU).
69. What are the factors affecting the properties of polyurethane elastomers from the perspective of molecular structure?
A: From the point of view of molecular structure, polyurethane elastomer is a block polymer, generally composed of oligomer polyols flexible long chain soft segment, diisocyanate and chain extender to form a hard segment, hard segment and soft segment alternate arrangement, forming a repetitive structural unit. In addition to containing ammonia ester groups, the polyurethane can form hydrogen bonds within and between molecules, and the soft and hard segments can form microphase regions and produce microphase separation. These structural characteristics make polyurethane elastomers have excellent wear resistance and toughness, known as "wear-resistant rubber".
70. Performance difference between ordinary polyester type and polytetrahydrofuran ether type elastomers
A: Polyester molecules contain more polar ester groups (-COO-), which can form strong intramolecular hydrogen bonds, so polyester polyurethane has high strength, wear resistance and oil resistance.
The elastomer prepared from polyether polyols has good hydrolysis stability, weather resistance, low temperature flexibility and mold resistance. Article source/Polymer learning Research
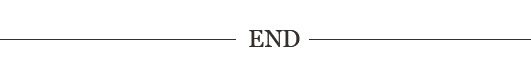
Post time: Jan-17-2024

